RO (Reverse Osmosis)
RO (Reverse Osmosis): Osmosis – Tendency of solvent having lower concentration of solute to move towards a solvent having a higher concentration of solute via a semi-permeable membrane.
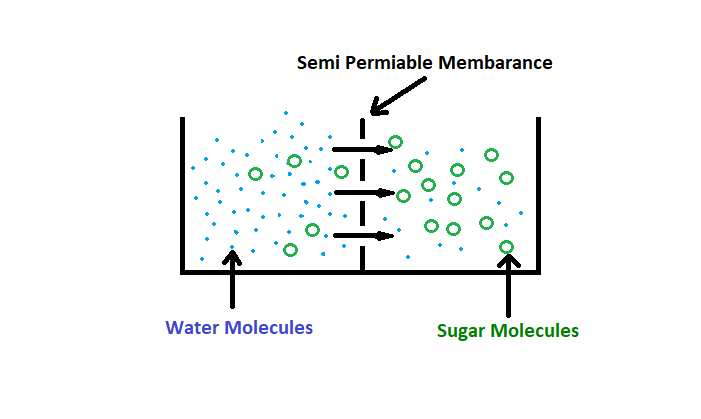
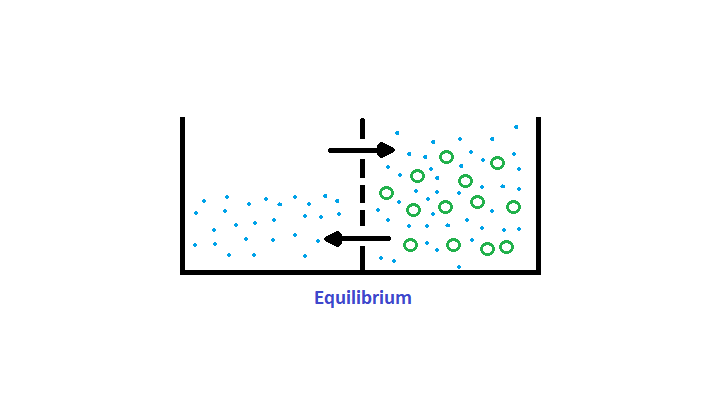
Osmosis gives rise to what we call ‘Osmotic Pressure’.
Osmotic Pressure refers to how hard water could ‘push’ to get through the barrier in order to diffuse to the other side.
Reverse Osmosis: It works by reversing the principle of Osmosis. When in a solution of solvent (water) and mixed molecules, only the pure solvent (water) is allowed to pass through a porous, semi-permeable membrane, filtering the larger solute molecules, the method is called Reverse Osmosis.
Here, the pressure applied to press the solute molecules through the semi-permeable membrane is greater than the osmotic pressure. The solvent (water) molecules moves from a highly concentrated solution to a less concentrated solution, leaving behind impurities. The desired liquid is a pure solution with a very low content of solute present in it.

